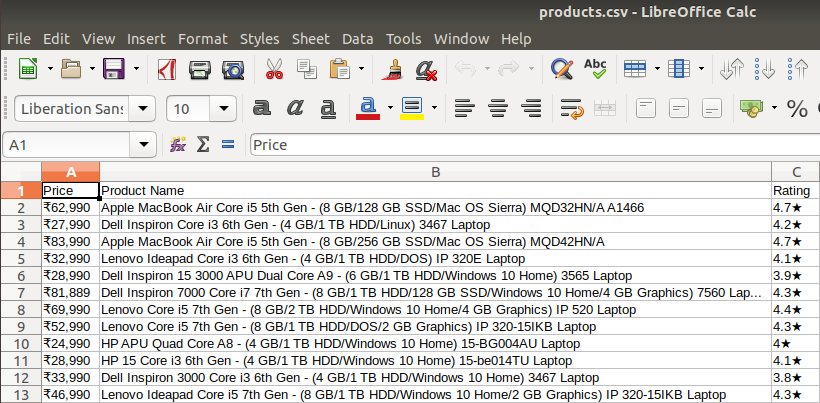
Sep 25, 2020 In this article, we will cover how to use Python for web scraping. We'll also work through a complete hands-on classroom guide as we proceed. Note: We will be scraping a webpage that I host, so we can safely learn scraping on it. Many companies do not allow scraping on their websites, so this is a good way to learn. Learn web scraping with R with this step-by-step tutorial. We will see the different ways to scrape the web in R through lots of example. In this article, we will cover how to use Python for web scraping. We'll also work through a complete hands-on classroom guide as we proceed. Note: We will be scraping a webpage that I host, so we can safely learn scraping on it. Many companies do not allow scraping on their websites, so this is a good way to learn.
- Python Web Scraping Tutorial
- Define the VBA variable and assign the data type as “Internet Explorer.” Code: Sub WebScraping.
- May 05, 2020 Learn web scraping with R with this step-by-step tutorial. We will see the different ways to scrape the web in R through lots of example.
- Python Web Scraping Resources
- Selected Reading
In this chapter, let us learn how to perform web scraping on dynamic websites and the concepts involved in detail.
Introduction
Web scraping is a complex task and the complexity multiplies if the website is dynamic. According to United Nations Global Audit of Web Accessibility more than 70% of the websites are dynamic in nature and they rely on JavaScript for their functionalities.
Dynamic Website Example
Let us look at an example of a dynamic website and know about why it is difficult to scrape. Here we are going to take example of searching from a website named http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/search. But how can we say that this website is of dynamic nature? It can be judged from the output of following Python script which will try to scrape data from above mentioned webpage −
Output
The above output shows that the example scraper failed to extract information because the <div> element we are trying to find is empty.
Approaches for Scraping data from Dynamic Websites
We have seen that the scraper cannot scrape the information from a dynamic website because the data is loaded dynamically with JavaScript. In such cases, we can use the following two techniques for scraping data from dynamic JavaScript dependent websites −
- Reverse Engineering JavaScript
- Rendering JavaScript
Reverse Engineering JavaScript
The process called reverse engineering would be useful and lets us understand how data is loaded dynamically by web pages.
For doing this, we need to click the inspect element tab for a specified URL. Next, we will click NETWORK tab to find all the requests made for that web page including search.json with a path of /ajax. Instead of accessing AJAX data from browser or via NETWORK tab, we can do it with the help of following Python script too −
Example
The above script allows us to access JSON response by using Python json method. Similarly we can download the raw string response and by using python’s json.loads method, we can load it too. We are doing this with the help of following Python script. It will basically scrape all of the countries by searching the letter of the alphabet ‘a’ and then iterating the resulting pages of the JSON responses.
After running the above script, we will get the following output and the records would be saved in the file named countries.txt.
Output
Rendering JavaScript
In the previous section, we did reverse engineering on web page that how API worked and how we can use it to retrieve the results in single request. However, we can face following difficulties while doing reverse engineering −
Sometimes websites can be very difficult. For example, if the website is made with advanced browser tool such as Google Web Toolkit (GWT), then the resulting JS code would be machine-generated and difficult to understand and reverse engineer.
Some higher level frameworks like React.js can make reverse engineering difficult by abstracting already complex JavaScript logic.
The solution to the above difficulties is to use a browser rendering engine that parses HTML, applies the CSS formatting and executes JavaScript to display a web page.
Example
In this example, for rendering Java Script we are going to use a familiar Python module Selenium. The following Python code will render a web page with the help of Selenium −
First, we need to import webdriver from selenium as follows −
Now, provide the path of web driver which we have downloaded as per our requirement −
Now, provide the url which we want to open in that web browser now controlled by our Python script.
Now, we can use ID of the search toolbox for setting the element to select.
Next, we can use java script to set the select box content as follows −
The following line of code shows that search is ready to be clicked on the web page −
Next line of code shows that it will wait for 45 seconds for completing the AJAX request.
Now, for selecting country links, we can use the CSS selector as follows −
Now the text of each link can be extracted for creating the list of countries −
Want to scrape the web with R? You’re at the right place!
We will teach you from ground up on how to scrape the web with R, and will take you through fundamentals of web scraping (with examples from R).
Throughout this article, we won’t just take you through prominent R libraries like rvest and Rcrawler, but will also walk you through how to scrape information with barebones code.
Overall, here’s what you are going to learn:
- R web scraping fundamentals
- Handling different web scraping scenarios with R
- Leveraging rvest and Rcrawler to carry out web scraping
Let’s start the journey!
Introduction
The first step towards scraping the web with R requires you to understand HTML and web scraping fundamentals. You’ll learn how to get browsers to display the source code, then you will develop the logic of markup languages which sets you on the path to scrape that information. And, above all - you’ll master the vocabulary you need to scrape data with R.
We would be looking at the following basics that’ll help you scrape R:
- HTML Basics
- Browser presentation
- And Parsing HTML data in R
So, let’s get into it.
HTML Basics
HTML is behind everything on the web. Our goal here is to briefly understand how Syntax rules, browser presentation, tags and attributes help us learn how to parse HTML and scrape the web for the information we need.
Browser Presentation
Before we scrape anything using R we need to know the underlying structure of a webpage. And the first thing you notice, is what you see when you open a webpage, isn’t the HTML document. It’s rather how an underlying HTML code is represented. You can basically open any HTML document using a text editor like notepad.
HTML tells a browser how to show a webpage, what goes into a headline, what goes into a text, etc. The underlying marked up structure is what we need to understand to actually scrape it.
For example, here’s what ScrapingBee.com looks like when you see it in a browser.
And, here’s what the underlying HTML looks like for it
Looking at this source code might seem like a lot of information to digest at once, let alone scrape it! But don’t worry. The next section exactly shows how to see this information better.
HTML elements and tags
If you carefully checked the raw HTML of ScrapingBee.com earlier, you would notice something like <title>..</title>, <body>..</body etc. Those are tags that HTML uses, and each of those tags have their own unique property. For example <title> tag helps a browser render the title of a web page, similarly <body> tag defines the body of an HTML document.
Once you understand those tags, that raw HTML would start talking to you and you’d already start to get the feeling of how you would be scraping web using R. All you need to take away form this section is that a page is structured with the help of HTML tags, and while scraping knowing these tags can help you locate and extract the information easily.
Parsing a webpage using R
With what we know, let’s use R to scrape an HTML webpage and see what we get. Keep in mind, we only know about HTML page structures so far, we know what RAW HTML looks like. That’s why, with the code, we will simply scrape a webpage and get the raw HTML. It is the first step towards scraping the web as well.
Earlier in this post, I mentioned that we can even use a text editor to open an HTML document. And in the code below, we will parse HTML in the same way we would parse a text document and read it with R.
I want to scrape the HTML code of ScrapingBee.com and see how it looks. We will use readLines() to map every line of the HTML document and create a flat representation of it.
Now, when you see what flat_html looks like, you should see something like this in your R Console:
The whole output would be a hundred pages so I’ve trimmed it for you. But, here’s something you can do to have some fun before I take you further towards scraping web with R:
- Scrape www.google.com and try to make sense of the information you received
- Scrape a very simple web page like https://www.york.ac.uk/teaching/cws/wws/webpage1.html and see what you get
Remember, scraping is only fun if you experiment with it. So, as we move forward with the blog post, I’d love it if you try out each and every example as you go through them and bring your own twist. Share in comments if you found something interesting or feel stuck somewhere.
While our output above looks great, it still is something that doesn’t closely reflect an HTML document. In HTML we have a document hierarchy of tags which looks something like
But clearly, our output from readLines() discarded the markup structure/hierarchies of HTML. Given that, I just wanted to give you a barebones look at scraping, this code looks like a good illustration.
However, in reality, our code is a lot more complicated. But fortunately, we have a lot of libraries that simplify web scraping in R for us. We will go through four of these libraries in later sections.
First, we need to go through different scraping situations that you’ll frequently encounter when you scrape data through R.
Common web scraping scenarios with R
Access web data using R over FTP
FTP is one of the ways to access data over the web. And with the help of CRAN FTP servers, I’ll show you how you can request data over FTP with just a few lines of code. Overall, the whole process is:
- Save ftp URL
- Save names of files from the URL into an R object
- Save files onto your local directory
Let’s get started now. The URL that we are trying to get data from is ftp://cran.r-project.org/pub/R/web/packages/BayesMixSurv/.
Let’s check the name of the files we received with get_files
Example Web Scraping Method
Looking at the string above can you see what the file names are?
The screenshot from the URL shows real file names
It turns out that when you download those file names you get carriage return representations too. And it is pretty easy to solve this issue. In the code below, I used str_split() and str_extract_all() to get the HTML file names of interest.
Let’s print the file names to see what we have now:
extracted_html_filenames
Great! So, we now have a list of HTML files that we want to access. In our case, it was only one HTML file.
Now, all we have to do is to write a function that stores them in a folder and a function that downloads HTML docs in that folder from the web.
We are almost there now! All we now have to do is to download these files to a specified folder in your local drive. Save those files in a folder called scrapignbee_html. To do so, use GetCurlHandle().
After that, we’ll use plyr package’s l_ply() function.
And, we are done!
I can see that on my local drive I have a folder named scrapingbee_html, where I have inde.html file stored. But, if you don’t want to manually go and check the scraped content, use this command to retrieve a list of HTMLs downloaded:
That was via FTP, but what about HTML retrieving specific data from a webpage? That’s what our next section covers.
Scraping information from Wikipedia using R
In this section, I’ll show you how to retrieve information from Leonardo Da Vinci’s Wikipedia page https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leonardo_da_Vinci.
Let’s take the basic steps to parse information:
Leonardo Da Vinci’s Wikipedia HTML has now been parsed and stored in parsed_wiki.
But, let’s say you wanted to see what text we were able to parse. A very simple way to do that would be:
By doing that, we have essentially parsed everything that exists within the <p> node. And since it is an XML node set, we can easily use subsetting rules to access different paragraphs. For example, let’s say we pick the 4th element on a random name. Here’s what you’ll see:
Mac adobe premiere pro cc crack. Reading text is fun, but let’s do something else - let’s get all links that exist on this page. We can easily do that by using getHTMLLinks() function:
Notice what you see above is a mix of actual links and links to files.
You can also see the total number of links on this page by using length() function:
I’ll throw in one more use case here which is to scrape tables off such HTML pages. And it is something that you’ll encounter quite frequently too for web scraping purposes. XML package in R offers a function named readHTMLTable() which makes our life so easy when it comes to scraping tables from HTML pages.
Leonardo’s Wikipedia page has no HTML though, so I will use a different page to show how we can scrape HTML from a webpage using R. Here’s the new URL:
As usual, we will read this URL:
If you look at the page you’ll disagree with the number “108”. For a closer inspection I’ll use name() function to get names of all 108 tables:
Our suspicion was right, there are too many “NULL” and only a few tables. I’ll now read data from one of those tables in R:
Here’s how this table looks in HTML
Awesome isn’t it? Imagine being able to access census, pricing, etc data over R and scraping it. Wouldn’t it be fun? That’s why I took a boring one, and kept the fun part for you. Try something much cooler than what I did. Here’s an example of table data that you can scrape https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/United_States_Census
Let me know how it goes for you. But it usually isn’t that straightforward. We have forms and authentication that can block your R code from scraping. And that’s exactly what we are going to learn to get through here.
Handling HTML forms while scraping with R
Often we come across pages that aren’t that easy to scrape. Take a look at the Meteorological Service Singapore’s page (that lack of SSL though :O). Notice the dropdowns here
Imagine if you want to scrape information that you can only get upon clicking on the dropdowns. What would you do in that case?
Well, I’ll be jumping a few steps forward and will show you a preview of rvest package while scraping this page. Our goal here is to scrape data from 2016 to 2020.
Let’s check what type of data have been able to scrape. Here’s what our data frame looks like:
From the dataframe above, we can now easily generate URLs that provide direct access to data of our interest.
Now, we can download those files at scale using lappy().
Note: This is going to download a ton of data once you execute it.
Web scraping using Rvest
Inspired by libraries like BeautifulSoup, rvest is probably one of most popular packages in R that we use to scrape the web. While it is simple enough that it makes scraping with R look effortless, it is complex enough to enable any scraping operation.
Let’s see rvest in action now. I will scrape information from IMDB and we will scrape Sharknado (because it is the best movie in the world!) https://www.imdb.com/title/tt8031422/
Awesome movie, awesome cast! Let's find out what was the cast of this movie.
Awesome cast! Probably that’s why it was such a huge hit. Who knows.
Still, there are skeptics of Sharknado. I guess the rating would prove them wrong? Here’s how you extract ratings of Sharknado from IMDB
I still stand by my words. But I hope you get the point, right? See how easy it is for us to scrape information using rvest, while we were writing 10+ lines of code in much simpler scraping scenarios.
Next on our list is Rcrawler.
Web Scraping using Rcrawler
Web Scraping Example.html
Rcrawler is another R package that helps us harvest information from the web. But unlike rvest, we use Rcrawler for network graph related scraping tasks a lot more. For example, if you wish to scrape a very large website, you might want to try Rcrawler in a bit more depth.
Note: Rcrawler is more about crawling than scraping.
We will go back to Wikipedia and we will try to find the date of birth, date of death and other details of scientists.
Output looks like this:
And that’s it!
You pretty much know everything you need to get started with Web Scraping in R.
Web Scraping Example Using Python
Try challenging yourself with interesting use cases and uncover challenges. Download spotify music mac. Scraping the web with R can be really fun!
While this whole article tackles the main aspect of web scraping with R, it does not talk about web scraping without getting blocked.
If you want to learn how to do it, we have wrote this complete guide, and if you don't want to take care of this, you can always use our web scraping API.
Happy scraping.
